RCPT (Rapid Chloride Permeability Test)
RCPT (Rapid Chloride Permeability Test)
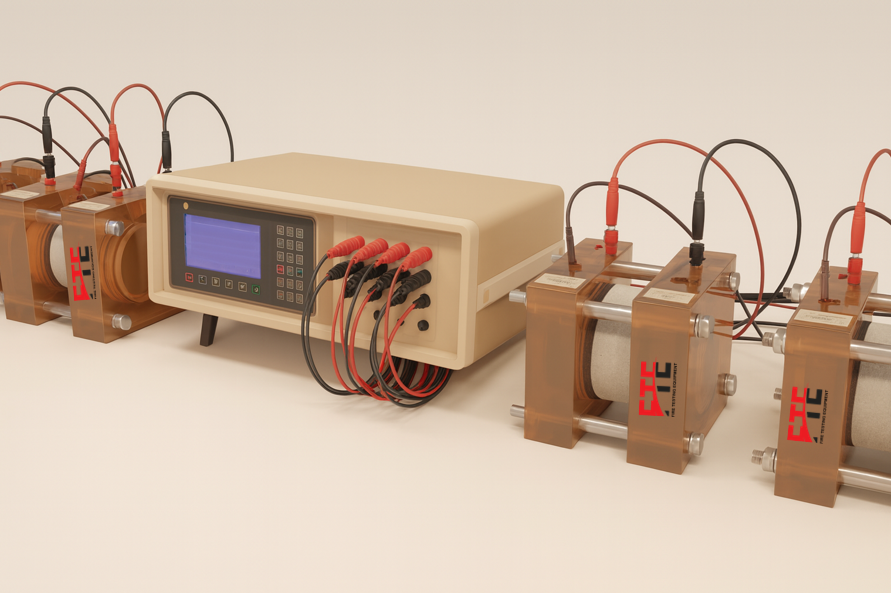
RCPT (Rapid Chloride Permeability Test) ASTM C 1202
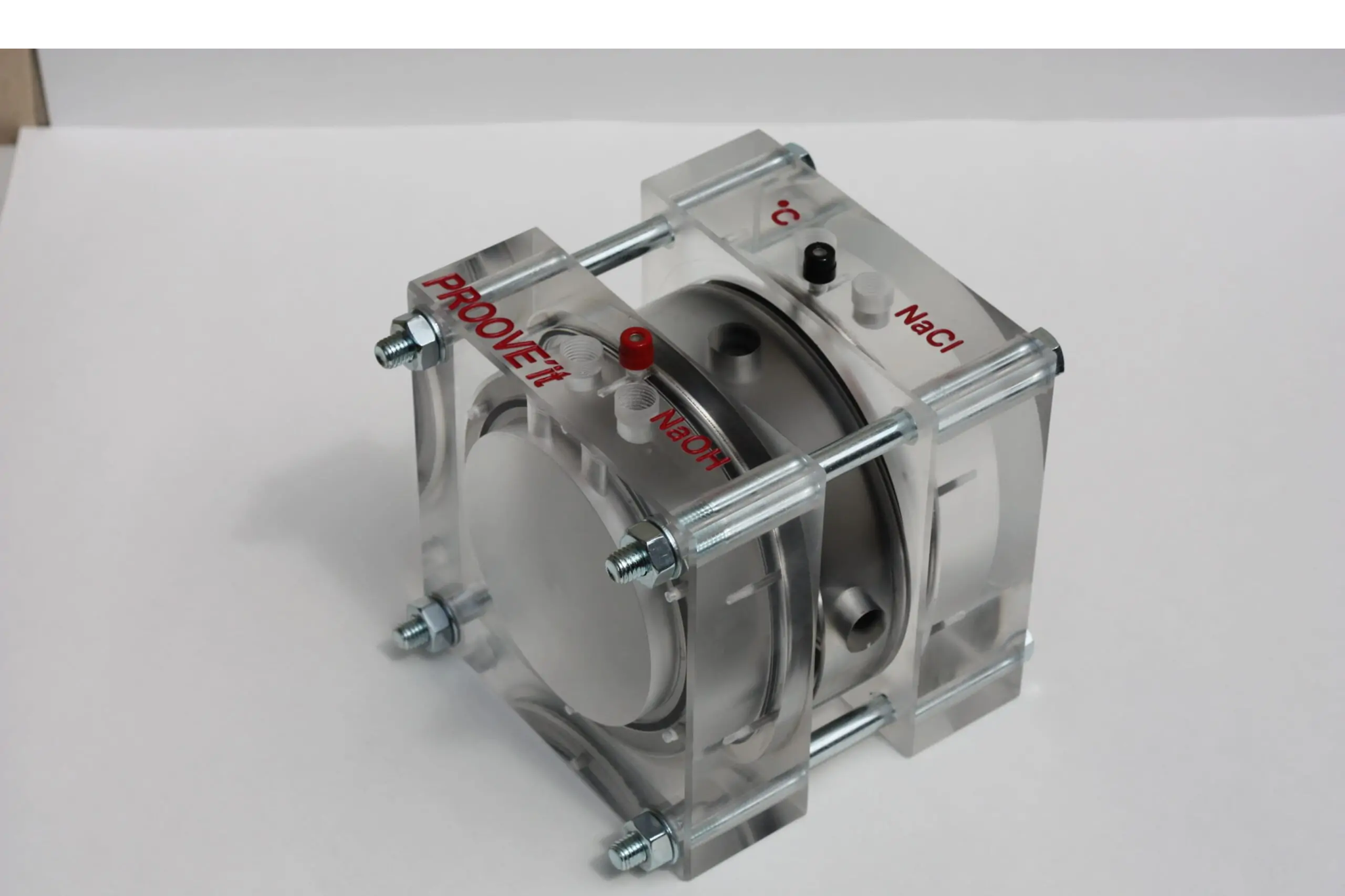
A RCPT (Rapid Chloride Permeability Test) with cell test standard, most commonly ASTM C 1202, is a test for evaluating a concrete's ability to resist chloride ion penetration using electrical indication. The test involves applying a constant DC voltage for six hours across a concrete specimen, measuring the total electrical charge (coulombs) that passes through it. A lower charge indicates higher resistance to chloride ingress, helping to predict the durability and service life of concrete structures
The RCPT Test Procedure (ASTM C1202)
-
Sample Preparation:
A cylindrical concrete specimen, typically 100 mm in diameter and 50 mm thick, is prepared.
-
Cell Assembly:
The specimen is placed in an RCPT cell with a leak-proof design, where a saturated NaCl solution is placed on one side and an NaOH solution on the other.
-
Electrical Application:
A 60-volt direct current (DC) is applied across the specimen for six hours.
-
Data Collection:
The current flow is continuously measured and recorded throughout the test.
-
Charge Calculation:
The total charge passed in coulombs is calculated by integrating the current over time.
Interpreting the Results
- High charge (more current): Indicates high permeability and poor resistance to chloride ions.
- Low charge (less current): Shows low permeability and good resistance to chloride ions, suggesting better durability.
Standardization
-
ASTM C1202:
This is the primary standard for the Rapid Chloride Permeability Test, also known as the Coulomb test.
-
AASHTO T 277:
Another standard that describes a similar test for concrete's resistance to chloride ion penetration.
Applications
- Quality Control: For durability-based quality control of new concrete.
- Performance Prediction: To predict the service life of concrete structures.
- Corrosion Protection: To assess the effectiveness of corrosion protection measures in concrete structures exposed to aggressive environments, such as marine structures or bridges.